Businesses today face the challenge of safeguarding transactions as they navigate the various intricacies of digital payments. Yet, the path to securing these transactions through PCI DSS 4.0 compliance can feel like a maze filled with complexities and uncertainties.
Such a pressing need for security, compounded by the risk of non-compliance, places pressure on many companies. However, you can achieve and manage compliance with the right approach.
In this article, we’ll discuss Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), its benefits, levels, requirements, and steps to achieve compliance.
What is PCI DSS compliance?
PCI DSS compliance is a framework that ensures all businesses that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card payments do so in a secure environment. Though not legally mandatory, major credit card companies enforce it to protect sensitive payment card information against security breaches and fraud.
The purpose of the PCI DSS compliance framework is to ensure that businesses that handle online payments have the necessary procedures and policies in place to protect confidential client data.
Some of the common PCI violations include weak access controls, insecure data transmission, insufficient network segmentation, and incomplete security policies, among others.
The primary objective of achieving PCI compliance is to lessen the likelihood of attacks. To do this, you need to use a secure Card Data Environment (CDE), whether you use your own environment or a secure payment option from a third party.
It’s becoming increasingly clear to consumers that making payments online comes with risks. For businesses to earn their trust, customers need to see that they value their privacy. In fact, 62% of consumers worldwide say fraud is an inevitable risk of shopping online, and 58% are uncomfortable submitting their banking information for online purchases.
When you demonstrate strict adherence to PCI DSS compliance requirements, you reassure your clients that your organization values and safeguards their data.
What are the benefits of maintaining PCI compliance?
Ensuring the security of sensitive information is a priority for any business.
In January 2023, 43% of identity theft victims wasted time resolving issues, while 33% had to freeze their credit cards. A robust security protocol is no longer optional but a necessity, especially with the increasing frequency of cyber attacks and staggering cost of data breaches. The average cost of a data breach is $4.45 million.
PCI compliance serves as a critical component in this security framework. Adhering to these standards is about meeting regulatory requirements and fostering a culture of trust and security.
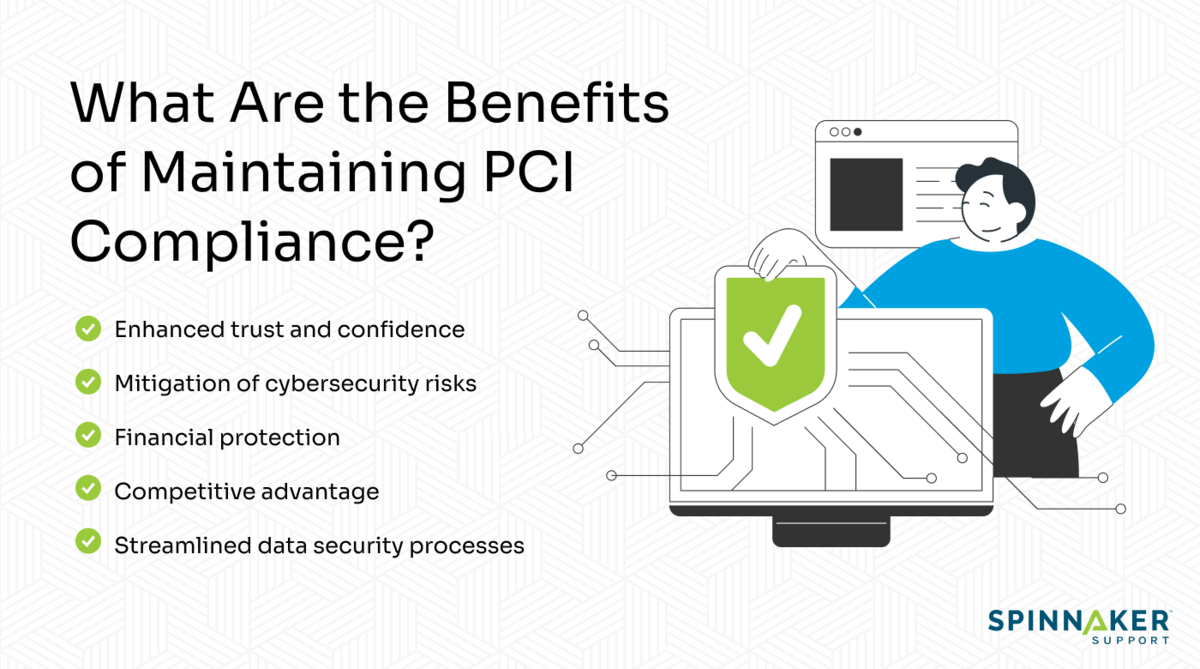
Here are the benefits of maintaining PCI compliance.
Enhanced trust and confidence
When consumers know a business complies with PCI DSS’ high security standards, their confidence in conducting transactions with that entity increases.
In June 2022, 54% of consumers said that they would trust a brand more if they could delete their data, and 48% said transparency over data leaks would boost trust.
Mitigation of cybersecurity risks
By rigorously following PCI DSS guidelines, companies aren’t just checking boxes but actively engaging in best practices for cybersecurity. The proactive stance and cybersecurity awareness allow for the early detection of vulnerabilities and the prompt implementation of corrective measures.
Financial protection
The financial ramifications of non-compliance can be staggering, including hefty fines and enduring damage to a company’s reputation. Achieving and maintaining PCI compliance serves as a protective shield, mitigating these potential financial setbacks.
Competitive advantage
Among the penalties for non-compliance with PCI DSS is restrictions on accepting payments from customers by credit card. Such limitations can cause huge financial losses, market share loss, and reputation damage. To process payments again, a company with this penalty must undergo a PCI reassessment by an external Quality Security Assessor (QSA).
Indeed, trust is a currency in today’s competitive marketplace. Companies that can showcase their commitment to data security through PCI compliance distinguish themselves from competitors.
Streamlined data security processes
Adopting PCI compliance is not just about adhering to a set of external standards; it’s also about internal optimization. Standardized data security measures provide a clear framework for businesses to structure their protection strategies.
What are the 4 levels of PCI DSS compliance?
To determine the scope of PCI DSS compliance, you first need to determine your company’s PCI compliance level.
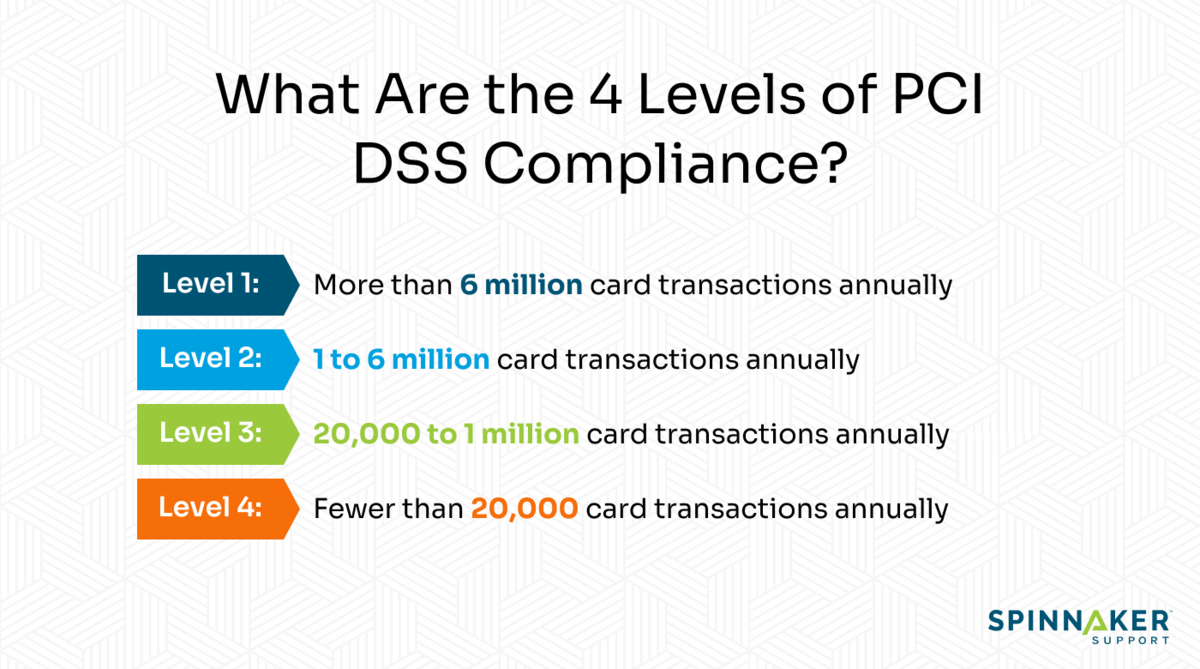
The following are the four PCI compliance levels.
Level 1 PCI DSS compliance
Level 1 compliance is for merchants processing over 6 million card transactions annually. A QSA must assess your organization if you meet this threshold. You also need to have quarterly vulnerability scans conducted by an Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV) to secure sensitive cardholder information. ASVs are organizations that provide security services and tools to perform external vulnerability scanning to verify compliance with PCI DSS requirements.
Level 2 PCI DSS compliance
Level 2 compliance targets businesses that process 1 to 6 million transactions every year. To fulfill your reporting requirements, you need to complete a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) and have an ASV scan your network. Ideally, a SAQ is a validation tool used by service providers or vendors to disclose the outcomes of their self-assessment under the PCI DSS.
Level 3 PCI DSS compliance
Level 3 compliance targets merchants who handle 20,000 to 1 million online transactions annually. To fulfill your level 3 grade controls and reporting requirements, you need to complete an annual SAQ. You also need to perform vulnerability scans with your preferred ASV.
Level 4 PCI DSS compliance
Essentially, this level applies to merchants that have fewer than 20,000 online transactions or as much as 1 million total transactions per year. Just like level 3 compliance, to fulfill your reporting requirements, you need to fill an SAQ and perform a network scan by an ASV.
What are the 12 PCI compliance requirements?
For organizations to be PCI DSS compliant, it’s mandatory to implement security policies, controls, and administrative processes that safeguard card information against unauthorized access.
A PCI compliance checklist includes following policies and implementing controls like installing a firewall, updating antivirus, and encrypting data transmission pathways.
Below, we present the updated list of requirements designed to ensure robust payment data security in this ever-changing digital environment.
Requirement 1: Install and maintain a firewall
The first requirement in protecting cardholder data from hackers is to set up and maintain firewalls. Firewalls scan all network traffic for indicators of suspicious activities that could jeopardize critical financial data.
Firewalls prevent unauthorized users from accessing your internal network systems by filtering outbound and incoming traffic.
Ideally, a firewall should:
- Safeguard any point-of-sale devices linked to wireless networks.
- Restrict access to authorized users only
- Reject all unwanted traffic automatically
- Log all changes, even those made by authorized users
Requirement 2: Don’t use vendor-supplied default passwords and settings
This PCI DSS requirement limits you from using the default credentials that vendors provide for software, firewalls, routers, point-of-sale systems, and more.
You should configure security settings instead of leaving them default. Using the manufacturer’s default password can make a system’s defenses much weaker because these are often well-known and easy for hackers to break.
Requirement 3: Protect cardholder data
To meet the PCI DSS requirement, you should apply encryption methods to protect sensitive data stored on systems or networks.
To offer comprehensive protection, organizations need to know the path that cardholder data takes as it moves through their systems, such as:
- Where cardholder data is stored
- Who has access to it, and
- Possible data processing techniques
You’re also required to conceal customers’ Personal Account Numbers (PANs). For example, you can mask the digits in customer credit cards, leaving only the last few numbers.
Requirement 4: Encrypt transmission of cardholder data
Encrypting cardholder data transmissions through public networks is essential in maintaining the confidentiality of personal information as it moves through less secure environments. The challenge, however, is that hackers can use different techniques, like packet sniffing or man-in-the-middle attacks, to intercept and steal cardholder data in transit.
To prevent unauthorized access to sensitive card information while it is in transit, you are required to employ robust encryption protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
Additionally, you can use secure protocols, like HTTPS or VPNs, for encryption, which is crucial for protecting cardholder information when sending it over public networks.
Further, many reputable third-party support providers employ strong cryptography standards to safeguard data in transit, ensuring any data captured by unauthorized individuals is useless.
Requirement 5: Protect all systems and networks from malicious software
Besides keeping antivirus software up to date, this requirement also calls for implementing a comprehensive strategy to combat potential security threats. To get the most benefits, you can think of partnering with a third-party support provider.
Their expert teams offer additional resources that can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to identify and mitigate potential security issues. For instance, Spinnaker Support offers consultation services for JD Edwards users on aspects such as OS, hardware upgrades, security implementations, tool upgrades, health checks, and more.
Requirement 6: Develop and maintain secure systems
This requirement is fundamental as it ensures that you fortify your applications against unauthorized exploitation. Requirement 6.3.3 is particularly critical, as it emphasizes the importance of using secure coding guidelines and reviewing code for vulnerabilities, especially for software developed by a third party. But while patching is an essential aspect of maintaining security, complete vulnerability management is more beneficial.
Consider the following table to see how vendor patching compares to vulnerability management:

According to PR Newswire and Dark Reading only 10% of these known vulnerabilities are addressed with vendor patches. And it’s taking organizations an average of 60 days to patch the critical risk vulnerabilities once a publisher provides the patch.
Reviewing CPU reports since 2010 will show that 36% of the patches provided are for vulnerabilities discovered in previous years. The time taken to address common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) is about 2 years.
Take a proactive approach to security by partnering with a third-party support provider like Spinnaker Support. Our highly qualified experts will assess your IT system and advise on any vulnerabilities or weaknesses we find to harden your systems. We can also help you maintain PCI-DSS compliance.
Requirement 7: Restrict access to cardholder data
You’re required to only grant access to cardholder data solely on a need-to-know basis. This ensures that only personnel with legitimate business reasons can interact with this sensitive data.
Additionally, as part of PCI DSS requirements, businesses must record their access control processes and examine their logs on a frequent basis.
Requirement 8: Authenticate access to system components
The requirement emphasizes the importance of distinguishing and verifying the identities of users accessing system components. Organizations can meticulously track user activities by allocating unique IDs for each individual who has computer access. This sensitive authentication approach enables a clear audit trail of who did what and when.
Requirement 9: Limit who can physically access cardholder data
Limiting physical access to sensitive cardholder data underscores the need to control who can physically interact with or view sensitive payment information.
For instance, you can use access codes or biometric access control to restrict physical access to data and assets. You’re also required to install electronic surveillance systems and keep recordings of these systems for at least 90 days.
Having strong access control measures allows organizations to take a crucial step in preventing unauthorized personnel from acquiring sensitive customer information.
Requirement 10: Track all cardholder data access
Monitoring any access point to network resources and the cardholder data environment is fundamental in establishing a detailed audit trail that records every interaction with sensitive information. Meticulously logging and reviewing all access to cardholder data and network resources allows companies to immediately identify, investigate, and respond to potential security violations.
Requirement 11: Regularly test processes and security systems
Every so often — at least once every three months — you should scan your external domains and IPs for potential entry points that hackers could exploit.
An intrusion detection system (IDS), like Snort and OpenVAS, can help you test your security systems by simulating attacks and letting you see how well your defenses work.
In fact, all systems and applications, whether developed in-house or provided by external vendors, should undergo rigorous and periodic security assessments.
Requirement 12: Maintain an internal policy that addresses information security
This requirement emphasizes the importance of establishing clear, comprehensive guidelines that govern the behavior of all individuals within an organization. There should be an internal infosec policy that safeguards the company’s workers, executives, and any outside vendors.
By developing and maintaining robust security policies, you can make sure that each member of the group knows their role in safeguarding sensitive information.
Check out our free PCI compliance checklist
Now that you’re familiar with the PCI DSS requirements, here’s a simple checklist you can use to check for compliance.
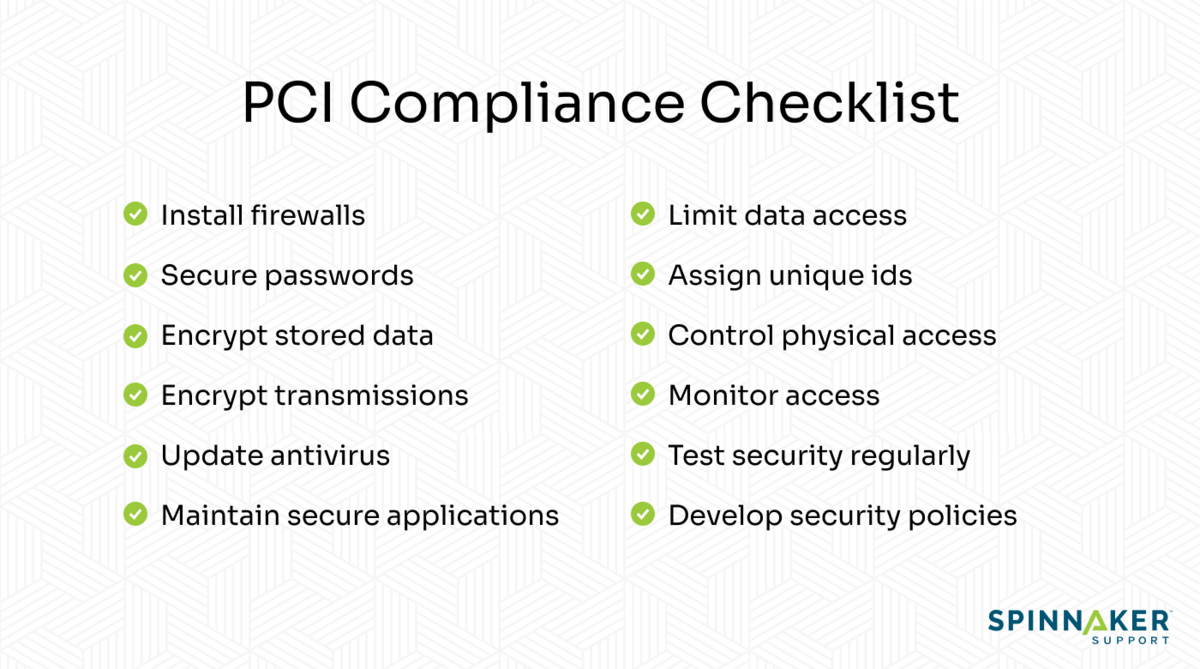
Use it to identify areas in your company that are already PCI-compliant or need improvement.
7 steps to become PCI DSS V4.0 compliant if you’re already V3.2 compliant
The most recent PCI DSS compliance framework, version 4.0, was released in March 2002, replacing version 3.2.
Companies that are already compliant with PCI DSS version 3.2 have until March 2024 to ensure compliance with Version 4.
Here are a few steps you can follow to transition from PCI DSS V3.2 to V4.0 compliance.
Step 1: Review V4.0 requirements
The first step is to become familiar with the new and updated requirements of the PCI DSS version 4.0. Learn how Version 4.0 differs from Version 3.2 and read the updated requirements carefully to make note of any changes from the previous version. This initial step is crucial for setting a clear compliance roadmap and prioritizing areas for improvement.
Step 2: Conduct a gap analysis
To find out how your present security measures compare to the requirements of V4.0 PCI, you should conduct a thorough gap analysis. Perform a comprehensive gap analysis to pinpoint any areas where your present compliance practices might not meet the requirements of Version 4.0.
Step 3: Update your security policies and procedures
You’ll need to revise your existing security policies and procedures to align with V4.0 standards. Adapt your business processes and policies to meet the demands of Version 4.0 and make sure that all relevant stakeholders are aware of these updates and that they adhere to them.
Step 4: Implement required changes
Start applying required changes by focusing on those labeled as high priority, according to the gap analysis. Timely implementation of these changes is key to maintaining continuous compliance and security.
Step 5: Educate and train your staff
Make sure that all relevant personnel know the new security requirements and understand their roles in maintaining compliance. Enhanced training guarantees that the workforce can effectively uphold updated security standards.
Step 6: Test and validate compliance
Conduct thorough testing of your systems and processes to ensure they meet V4.0 standards. Testing helps to verify the efficacy of the implemented changes and identifies any gaps in compliance. Additionally, keep all relevant records and reports up-to-date to prove compliance, and update your documentation to reflect Version 4.0 changes.
Step 7: Engage a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA)
If necessary, consult with a QSA to review your compliance with V4.0, as they can provide expert guidance and help identify any overlooked areas. Their insights are invaluable in improving your security measures and ensuring comprehensive compliance.
Free checklist to check for PCI DSS V4.0 compliance
Feel free to follow the steps outlined below to help you transition from PCI DSS V3.2 to V4.0 compliance.

How Spinnaker Shield can help with PCI compliance and audits
Spinnaker Support can help with PCI compliance and audits by offering a robust suite of security tools and services. They have designed this suite to identify and mitigate risks and security vulnerabilities, ensuring the payment environments of an enterprise are ironclad against breaches.
The dual capability of providing PCI compliance while also being adaptable to other regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA, makes Spinnaker Support crucial for security and compliance in enterprises.
You can effortlessly achieve regulatory compliance across your entire Oracle, JD Edwards, and SAP software footprint with Spinnaker. To top it all off, their team of specialists can advise you on which categories of vulnerabilities to focus on and how to reduce your attack surface.
Enhance PCI compliance with Spinnaker Support
Navigating the complex landscape of PCI compliance is crucial for protecting sensitive payment information and maintaining customer trust. The process of becoming PCI DSS compliant is thorough and may take a lot of time. In fact, you may find it challenging to keep track of your security posture and implement controls from the PCI DSS checklist.
Through Spinnaker Shield, Spinnaker Support provides an essential toolkit for identifying vulnerabilities, enhancing existing security protocols, and ensuring compliance with PCI DSS V4.0 standards and audits. Want to learn more? Contact us to schedule a consultation!

