Customers expect companies to deliver reliable digital services with minimal disruptions. But meeting these expectations isn’t easy without the right IT processes.
This is where IT Service Management (ITSM) comes in — a set of processes that dictate how you design, deliver, and manage the delivery of IT services to your customers.
In this article, we’ll explain what ITSM is and the processes it encompasses. Then, we’ll cover ITSM best practices for each process. We’ll also look at how you can implement these best practices in an efficient and cost-effective manner by partnering with a managed service provider.
What is ITSM?
ITSM stands for Information Technology Service Management. It refers to companies’ best practices and processes to design and deliver IT services.
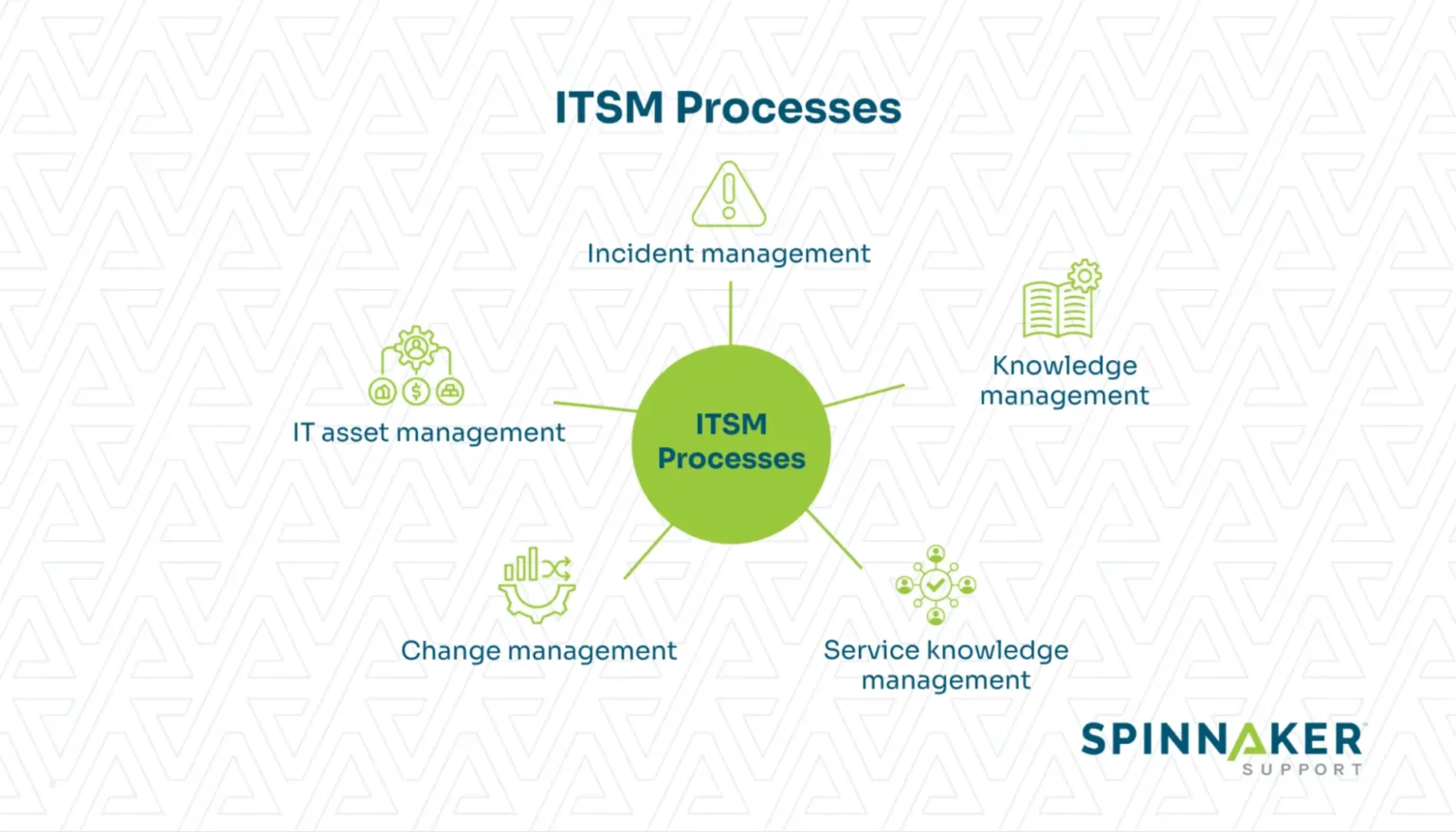
ITSM encompasses a variety of related processes, including:
- Incident management
- IT asset management
- Change management
- Service level management (SLM)
- Knowledge management
So, why is it essential to implement ITSM best practices?
ITSM best practices help companies align their IT services with their objectives, from improving customer satisfaction with faster response times to minimizing service disruptions. It can also:
- Create standardized and repeatable IT processes
- Improve the quality of IT service delivery
- Mitigate risks associated with IT services
- Foster collaboration between IT teams and stakeholders
- Drive continuous improvement in IT service delivery
The next few sections cover ITSM best practices for various processes. Implement these to enhance efficiency, improve productivity, and deliver better customer experiences.
ITSM incident management best practices
Incident management is the process of investigating and responding to incidents that may degrade service or prevent users from accessing IT. Examples include hardware failures that cause system outages and software updates that break critical functionalities.
Here are ITSM best practices to create a well-defined incident management process.
1. Create and test an incident response plan
The first step to resolving incidents promptly is to create an incident response plan — a document that lays out the exact steps that IT teams will follow in the event of an incident.
While this may sound obvious, only 27% of organizations have incident response plans, and only 63% regularly test them.
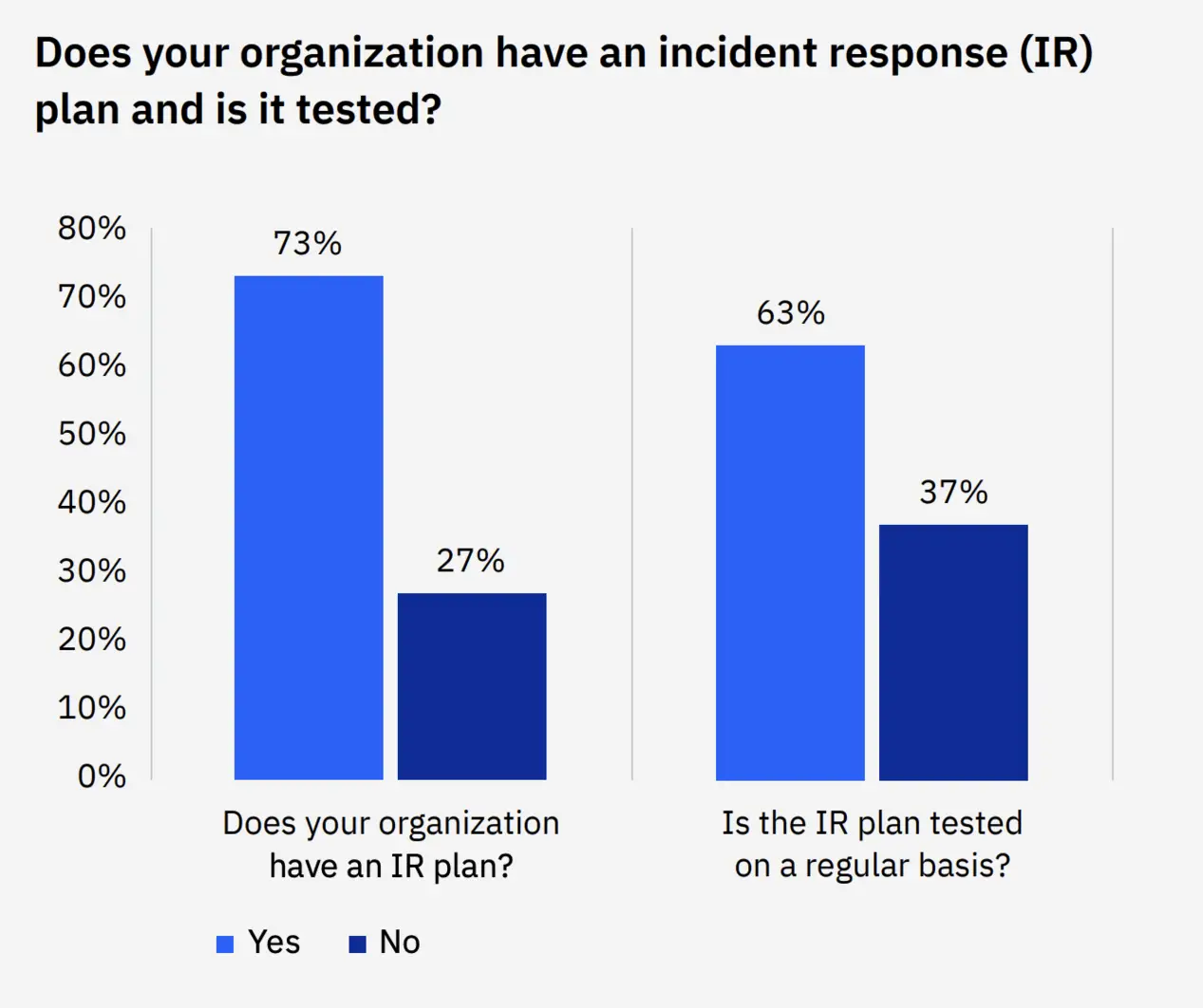
A well-defined incident response plan will help restore normal operations quickly and prevent future occurrences.
A typical incident response plan follows five steps:
- Preparation: Establish an incident response team and define roles and responsibilities for each member. Conduct risk assessments and develop “playbooks” to standardize procedures for potential threats.
- Detection: Monitor your IT systems using network monitoring tools to detect security issues. Analyze incidents to determine their scope and priority level.
- Containment: Contain potential threats to prevent further damage. This can involve isolating affected systems, patching vulnerabilities, and changing user credentials.
- Recovery: Work towards restoring normal operations. This can include restoring data from backups and implementing additional security measures.
- Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis to understand the root cause of an incident. This is where you’ll determine what worked and what didn’t in your response plan.
Finally, regularly test your incident response plan and review performance metrics to identify the areas you can improve.
2. Use automation tools to improve efficiency
Managing tickets manually isn’t the best use of your time. It’s also more prone to errors, which makes the use of automation tools more critical.
For example, PagerDuty allows you to set up workflows that automatically route tickets to the right teams and loop in relevant stakeholders.
Network monitoring tools allow you to respond and resolve incidents before they escalate. Of course, managing an on-premise solution isn’t easy. Such systems typically require specialized training to become familiar with their functionalities.
An alternative is to work with a managed service provider like Spinnaker Support. We continuously monitor your systems, which allows us to quickly respond to incidents and provide status updates to relevant stakeholders.
IT asset management best practices
IT asset management refers to overseeing an organization’s assets throughout each stage of its lifecycle. Assets can include hardware and software licenses.
Here are two best practices for managing your IT assets.
3. Establish processes for each stage of the IT asset lifecycle
IT assets typically go through five stages: Plan, Acquire, Deploy, Maintain, and Dispose. The exact steps can vary for each organization but generally follow the same format.
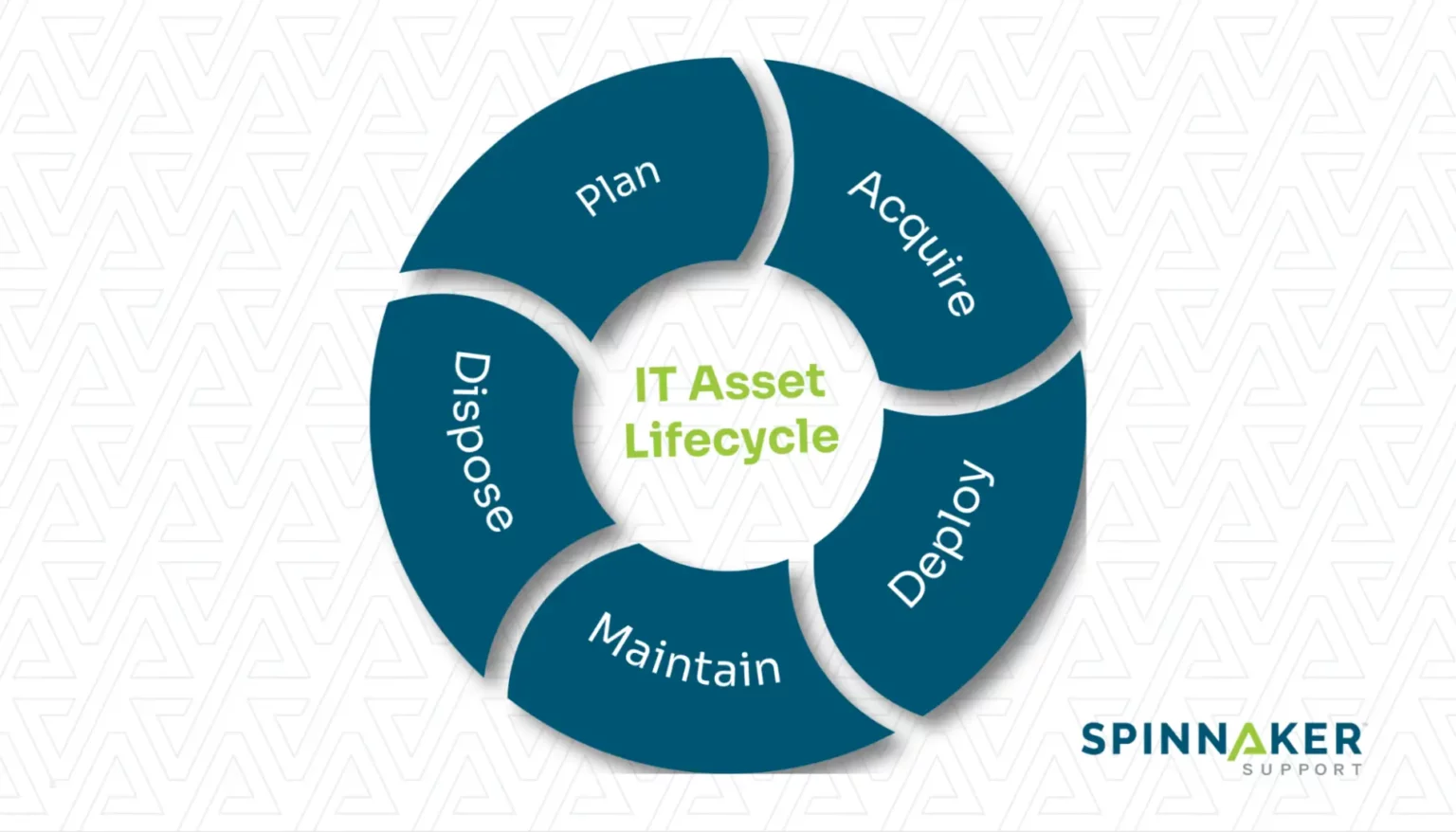
Establishing clear processes for each stage can help:
- Optimize asset utilization and reduce cost
- Inform decisions around upgrades and replacements
- Mitigate risks associated with theft or unauthorized access
- Ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements
- Improve system reliability and minimize downtime
An example of a process for the planning stage of an asset might look like:
- Identify asset needs
- Define asset requirements
- Research and evaluate options
- Perform a cost-benefit analysis
- Seek approval from relevant stakeholders
Defining clear processes for the IT asset lifecycle will help your organization establish a systematic approach to acquiring assets that align with business objectives.
4. Monitor software licenses to ensure compliance
Software vendors like Oracle and SAP conduct audits to ensure companies adhere to their license terms. Non-compliance can incur heavy penalties and even legal action. Over the past few years, nearly a quarter of organizations have paid over a million dollars in fines.
Use license management tools to monitor and track the usage of software licenses within your company. They can also track expiration dates and identify instances of non-compliance, such as using more licenses than are available.
At Spinnaker Support, we offer services to help companies ensure software license compliance and even protect against ongoing audits. These include license readiness reviews, audit defense services, and compliance assurance checks.
Learn why moving to third-party support won’t trigger a software audit.
Change management best practices
Change management is the process of planning and implementing new changes in an organization. Examples include adopting new software and updating key processes.
Here are a couple of best practices for change management.
5. Establish a Change Advisory Board (CAB) to oversee changes
Just 30% of change initiatives achieve desired outcomes.
One way to help new initiatives succeed is establishing a CAB — a group of key stakeholders who plan, review, and implement proposed changes. These individuals provide guidance and oversight throughout the change management process.
For example, let’s say your company plans to adopt a new CRM. The CAB can help ensure a smooth rollout by:
- Evaluating how a new CRM aligns with the organization’s overall strategy
- Assessing the potential risks of the new software
- Developing mitigation strategies to address challenges
- Communicating with stakeholders throughout the implementation process
- Producing relevant materials and providing ongoing support to employees
- Measuring the impact of proposed changes and making adjustments
Instead of rolling out a change and hoping for the best, establishing a CAB can significantly increase the success rate of a new initiative.
6. Continuously monitor and review changes
To understand the impact of any changes you wish to implement, reviewing and analyzing relevant metrics to assess their impact regularly is essential.
Start by defining an objective, but be as clear and specific as possible. For example, if you’re implementing a change to improve resolution times, you might set the following objective: “Reduce average resolution times by 20% within a year.”
Then, establish a baseline and collect relevant data. This will help you measure the impact of a new initiative and make informed decisions on whether to keep or revise a change.
The people most affected by a change generally have the most feedback to provide. Be sure to seek input from your employees and implement their feedback. This shows your employees that you value their opinions.
Service level agreements (SLA) best practices
An SLA is a contractual agreement between a service provider and a customer. It helps set clear expectations regarding the services and quality of support a customer can expect.
Follow these best practices to create effective SLAs.
7. Create different SLAs
One SLA won’t fit every situation. You can create three types of SLAs: Customer-based, Service-based, and Multi-level.
Here’s a look at each type:
- Customer-based SLA: A customer-based SLA is used for individual customers and provides expectations in more detail. It covers each party’s responsibilities, escalation procedures, and more.
- Service-based SLA: A service-based SLA covers a company’s specific service. One example is a web hosting service providing an SLA of 99% uptime.
- Multi-level SLA: For multi-level SLAs, different levels of services are defined for different customer segments. An example includes providing one-hour response time for high-priority customers and two-hour response times for standard-priority customers.
Another type is an internal SLA, in which a company sets a level of service internally. For example, our SLA mandates quick response times (less than 15 minutes) for incoming tickets.
8. Regularly monitor and report SLA performance
Monitor SLA performance to identify areas of improvement and maintain transparency when it comes to service delivery. SLA metrics you can monitor include:
- Response time
- Resolution time
- Availability of service
- Customer satisfaction
Use ITSM tools to continuously collect key performance indicators (KPIs) related to SLA performance. This will help automate data collection and generate reports that you can provide to relevant stakeholders. Then, use the insights you gain to improve your SLAs continuously.
For example, let’s say your response times aren’t improving. To remedy this, you must identify and address any bottlenecks that contribute to delayed responses, such as inefficient communication channels or unclear procedures. You can implement an incident management system to facilitate faster responses in this case.
Knowledge management best practices
Knowledge management is the process of capturing and facilitating access to knowledge that key stakeholders within an organization can easily engage with.
Here are a few best practices for knowledge management.
9. Establish processes to capture and document knowledge
An estimated 79% of employees believe they could be more efficient.

One way to help your employees become more efficient is to have processes to capture and store knowledge. This way, your team won’t waste valuable time searching for information they need to do their work.
Use software tools like Nuclino or Notion to create an internal knowledge base that users can contribute to. This ensures valuable information isn’t lost if an employee leaves. These tools can also help onboard new employees and quickly get them up to speed.
10. Integrate knowledge management systems with ITSM tools
Integrating knowledge management systems with ITSM tools can help optimize service delivery and improve efficiency. It can also ensure that relevant knowledge is readily accessible.
Integrations can help IT support teams:
- Quickly identify and resolve incidents
- Conduct problem and root cause analysis
- Make more informed decisions
The first step is to identify an integration approach, which will depend on your organization’s requirements and ITSM capabilities. Configure integration settings within both systems and conduct thorough testing to ensure data flow. Provide training and education to IT teams to ensure they know how to utilize the integration effectively.
Spinnaker Support for ITIL-centric services
ITSM best practices can improve the delivery and quality of your IT services. You can implement them by hiring an internal IT team and training them on ITSM practices, but this requires large investments of time and money. A more cost-effective option is to outsource your IT operations to a managed service provider.
Here’s what you get with Spinnaker Support:
- Access to dedicated experts: Spinnaker Support offers various managed services ITIL Level 2 and 3 engineers perform. We can also bring on Level 4 engineers for more complex issues.
- Flexibility and scalability: Every business has different requirements. We can tailor service plans to meet your organization’s specific needs and requirements.
- Support for custom code: Vendors like Oracle and SAP don’t support custom code, so you’ll need to look elsewhere for custom code-related issues. That’s not the case with us. Our team can help troubleshoot and fix issues even if your applications run custom code.
- Robust security: Keeping your IT systems secure is key to maintaining uptime. That’s why we deliver an extensive Seven-Point Security Solution that protects your IT infrastructure against cyber threats.
- 24/7 support: We offer around-the-clock support and respond within minutes. Our support engineers are always available to help address issues and minimize downtime.
By working with a managed service provider like Spinnaker Support, your company can also free up internal resources to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Conclusion
Implementing ITSM best practices can help organizations improve the delivery and quality of their IT services. It can also enhance operational efficiency and increase customer satisfaction.
One option to implement these best practices is with an internal IT team. Another is to work with our team of experts. We support Oracle, SAP, JD Edwards, and more, allowing you to get the full value out of your enterprise software. We also provide a range of managed services that allow you to offload your IT operations to our team.
Contact us today to discuss your IT requirements.


