Siloed business operations are a serious problem, with only 22% of business leaders saying their teams share data well. The negative impacts include less effective information sharing, lower data quality, and reduced productivity.
The only way to address this issue decisively is with tools like enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems that allow business departments and stakeholders to break down the silos.
This article will discuss some ERP system examples you can use in your business, but let’s cover the basics first.
What is enterprise resource planning (ERP)?
Companies use ERP software systems to manage processes across various departments with functions such as automation, standardization, reporting, and data management. It allows data to flow from and between different parts of the business, including financial management, HR, procurement, and inventory management.
In the past, ERP systems were specialized for each business segment, creating even more siloed operations even if they improved processes in their dedicated areas. Most ERP solutions today consolidate data to provide a single source of truth that allows all departments to work together towards common business goals.
What is the difference between CRM and ERP?
CRM is short for customer relationship management, and it differs from ERP in that it focuses on managing customer interaction, whereas ERP focuses on running business operations.
It helps to think of CRM as front-office operations such as sales, marketing, and customer success, and ERP as back-office operations such as HR, finance, and supply chain management.
That said, many ERPs have a CRM module, making it easier for more areas of the business to work together towards all-around growth.
What are the benefits of ERP?
Some of the advantages of adopting ERP software for your business include the following.
Let’s take a closer look.
- Improves cross-team collaborationERP systems break down business silos by consolidating data from various departments into a central database easily accessible to other teams. Because they don’t have to manually share information after they’ve generated it, the teams on the ERP can collaborate more easily just by participating in their business functions.
- Increases productivityDepartments can simply do more because they have access to a larger pool of information and raw data with an ERP system. If you opt for one with cloud functionality, you also remove location-based barriers to productivity for all your teams.Project managers can also maintain a strong grasp of operations across different business areas when they can access these systems.
- Increases efficiencyOne key feature of ERP software is the ability to automate processes, allowing you to reduce the amount of time spent on repetitive and low-level tasks across the business. This way, you free up team members to focus on other areas of operation, resulting in markedly improved efficiency across the board.
- Stronger data and information managementAs different departments operate as usual, the data they generate flows into a centralized location where it’s easier for system admins and personnel in similar roles to stay on top of it, whether they intend to repurpose it in the future or keep it contained as a security measure.
- Better cost managementWith a good enough ERP, you get modules that cover different areas of the business, including finance, HR, logistics, manufacturing, customer success, and supply chain management. This setup means you can rein in operational costs as you don’t pay for each separately.
- Strengthens securityERP systems have strong role-based access control features that ensure data is only attainable to authorized parties. This way, you get the full benefits of cross-team data flows but not in a way that’s uncontrolled, whereby sensitive information moves freely and can fall into the wrong hands, malicious or not.
- Improves scalabilityMost ERPs can process large amounts of data, enforce complex logic and workflows, and accommodate thousands of users across a company. If you’re looking at cloud-based ERP systems, you could cover the globe and remove most virtual and physical barriers to scaling.
- Easier to maintain complianceERPs can process the data they collect to generate accurate reports, logs, and audit trails that you can submit to any regulatory body that requires them from your company. There’s a range of areas where this can come in handy, with one of the most obvious scenarios being using the financial reporting functions to keep up with tax requirements in your respective jurisdictions.
What are the 5 components of ERP?
ERP systems come with smaller specialized applications called modules that are designed to cater to specific processes and departments.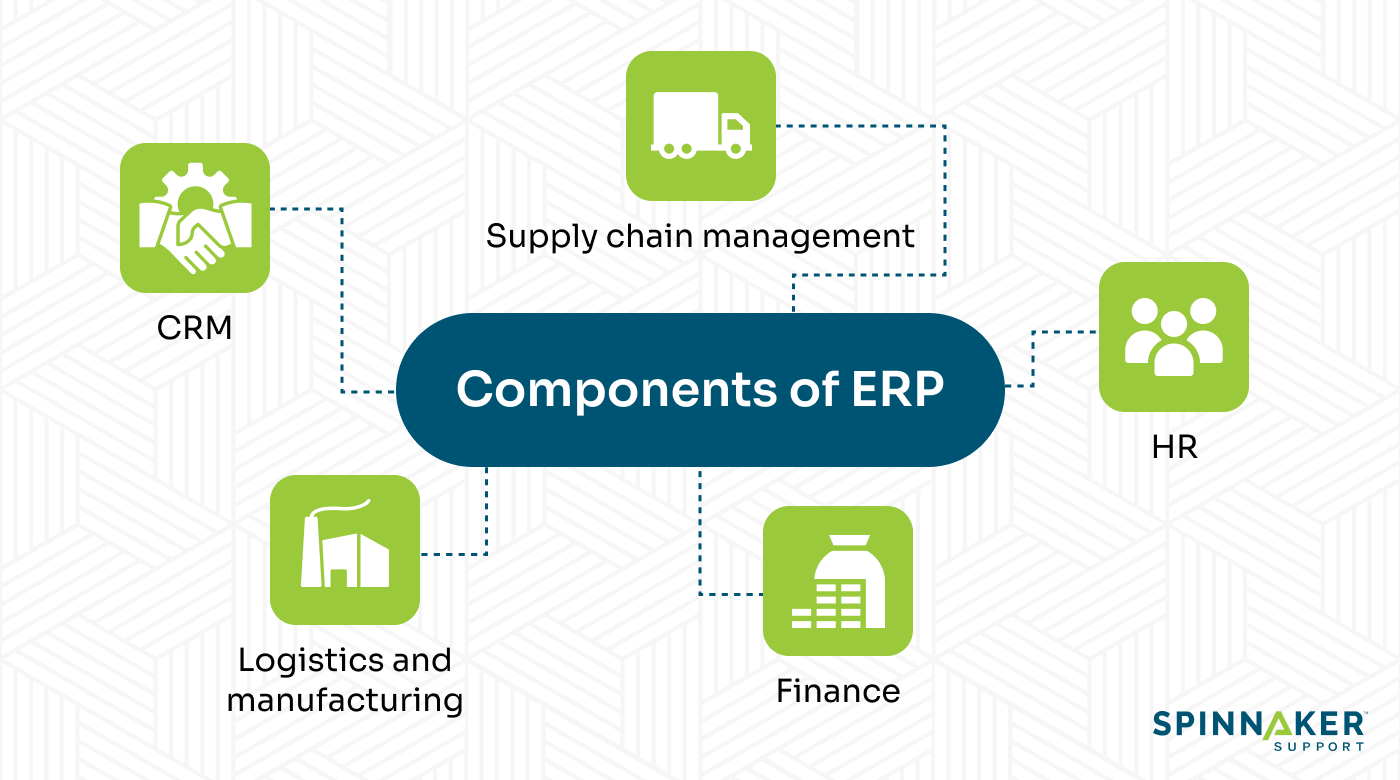
There are several such components, but here are the major ones you’ll almost always find in any ERP.
- FinanceAs the name suggests, this module is targeted primarily toward accounting departments. One major function they provide is the ability to monitor your company’s cash flow so you’re not caught off guard by financial constraints.
It also tracks customer payments by collecting invoices in one place for you to process in bulk. You can also use the finance module to manage your budgets by looking at historical trends to forecast future spending and leveraging its reporting capabilities to generate proposals. - Human resources managementSometimes referred to as human capital, this module allows you to manage employee data. At the base level, it’s a database that contains a list of the people that work at the company along with other details. It can also include information such as actual versus expected performance, changes in compensation, recruitment costs, and benefits programs.This might also be the module in charge of day-to-day staffing and time tracking, and it’s usually the one that handles employee payments over the finance component.
- Supply chain managementThis module, sometimes referred to as procurement, is for businesses to keep track of their relationships with suppliers. You can connect it to their databases, so you always have an updated list of what’s available.
If your business is the supplier, this module is still the one you’d use to control your supply chain because it also provides portals for managing fulfillments and keeping an eye on what’s in warehouses. - Logistics and manufacturingWhile some ERPs might separate these modules depending on who their target audience is, you might also find them grouped together because they often serve overlapping functions, including warehouse and inventory management.
They’re for companies that run manufacturing plants or large-scale deliveries to track all of that information in one place. They also often extend into quality control to ensure customer satisfaction and higher rates of retention. - Customer relationship managementDepending on the provider’s niche and business model, this module might be an entirely different product, but a lot of ERPs have it as a draw for companies that are worried about sprawl and want to keep their stack as light as possible.
As discussed previously, a CRM component focuses on the front-office aspects of the business, with functions such as sales, marketing, and customer success. It might also have additional functions such as ticket, service, and case management.
What are some examples of ERP systems?
ERP systems are several decades old at this point, so there are several options from large, medium, and small providers alike. Spinnaker Support provides management and migration services for several of the most popular ERP system examples, including the following:
- Microsoft Dynamics
 Microsoft Dynamics is a suite of business applications with a strong ERP component. It provides different modules in this category, including Finance, Project Operations, Business Central, Supply Chain Management, Intelligent Order Management, Commerce, and Fraud Protection.It connects to other Microsoft products and services to allow you to increase its functionality, including Cloud for storage, Power Platform for low-code app development, and 365 for productivity apps such as Word and Excel.
Microsoft Dynamics is a suite of business applications with a strong ERP component. It provides different modules in this category, including Finance, Project Operations, Business Central, Supply Chain Management, Intelligent Order Management, Commerce, and Fraud Protection.It connects to other Microsoft products and services to allow you to increase its functionality, including Cloud for storage, Power Platform for low-code app development, and 365 for productivity apps such as Word and Excel.
All these combined make it a comprehensive ERP solution that commands a leading market share of 87%. - JD Edwards EnterpriseOne
 EnterpriseOne is an ERP system from Oracle provided under the JD Edwards brand, one of the oldest players in the industry, which the company acquired in 2005.It’s very flexible, with support for multiple popular databases (SQL, IBM Db2, and Oracle), virtual machines (VMware and Oracle VM), and operating systems (Windows, Linux, IBM I5OS, and AIX).
EnterpriseOne is an ERP system from Oracle provided under the JD Edwards brand, one of the oldest players in the industry, which the company acquired in 2005.It’s very flexible, with support for multiple popular databases (SQL, IBM Db2, and Oracle), virtual machines (VMware and Oracle VM), and operating systems (Windows, Linux, IBM I5OS, and AIX).
Aside from the usual ERP modules, it provides useful functions for asset lifecycle management and localization. With asset lifecycle management, you can control operations and derive real-time insights from assets such as equipment and manufacturing plants.
Localization allows you to run operations globally by accounting for varying regional financial and regulatory requirements. Aside from North America, it supports localization in countries in the EMEA, LATAM, and JAPAC regions.
- SAP Business Suite 7
SAP Business Suite 7 is one of SAP’s longest-running offerings, with nearly 20 years of operation, during which it’s consistently stood out as one of the most comprehensive ERPs out there. It’s made up of a collection of robust business products that include SAP ERP 6.0, CRM 7.0, SRM 7.0, SCM 7.0, and PLM 7.0.SAP has announced its plans to stop direct maintenance in 2027, but for businesses that don’t want to move the arguably more restrictive S/4HANA, you can get a third party like Spinnaker Support to manage the system on your behalf. - Oracle EBS
Oracle E-Business Suite, EBS for short, provides several ERP modules that are optimized for Oracle Cloud but can still run on other platforms, including on-prem. Oracle is currently pushing customers to move to Fusion Cloud ERP, but, as we mentioned above, you can stick with this version and maintain more control over your system by choosing your own management team.
What makes an ERP implementation successful?
A successful ERP implementation comes down to the execution, something that differs between companies depending on factors like their size and requirements. For this reason, it’s best that you have an experienced team on your side from the start.
Spinnaker Support has extensive experience under its belt and has taken several businesses through their ERP journey, from initial consultation through to management and support.
Take the story of Autodesk, a multibillion-dollar company that provides industry-leading 3D software solutions, which nevertheless struggled to get SAP to follow through on the pricey support services they were paying for. After weighing their options, they chose Spinnaker Support for a painless transition to a more reliable team at a fraction of the cost.
We’re happy to report that Autodesk is still a loyal and satisfied customer. They were able to reinvest their savings into the business and are considering using Spinnaker Support for more services.
Conclusion
ERP software allows businesses to break their departments out of silos to improve cross-team collaboration and customer service delivery. These solutions have five major components that target operations in finance, HR, manufacturing and logistics, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
If you’re ready to improve your core business processes, contact a support specialist from Spinnaker Support to discuss the best third-party support and managed services for your ERP. We handle some of the most popular examples of ERP systems from providers like Oracle, SAP, Microsoft, and JD Edwards.


