Quick Summary
We’ve created a guide to break down Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and show you how to integrate the ERP system into your organization.
Introduction
Does your organization struggle with disjointed processes and inconsistent information? Disconnected systems can decrease operational efficiency, create blind-spots in decision-making, and hinder the delivery of excellent customer experiences.
But fear not, as the solution lies in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integration. By unifying your ERP software with other systems and applications throughout your organization, you’ll streamline processes and empower accurate data-driven decisions.
We created this comprehensive guide to walk you through the essentials of enterprise resource planning and offer guidance for ensuring successful ERP integrations. Whether you’re new to ERP integration or want to build on your existing processes, this guide will help. Let’s dive in!
What’s enterprise resource planning (ERP)?
At the heart of modern business management, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a software solution that aims to provide a comprehensive solution for business management by collecting multiple departments and operations under a single digital umbrella. This unified approach facilitates communication, data sharing, and process automation.
Projected to exceed a remarkable $49 billion by 2027, the ERP market is building the digital backbone for companies in every sector from materials to manufacturing to retail.
Essential components of an ERP system
An ERP system typically consists of several key modules, each tailored to address specific business functions. These include:
- Finance: This module manages all financial aspects of the organization, including accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human resources: The HR module handles employee data, payroll, benefits administration, performance management, and recruitment.
- Inventory management: This module tracks and manages inventory levels, minimizing inventory costs and ensuring goods are available when needed.
- Supply chain management: The supply chain module oversees the flow of goods and services from procurement to production to distribution.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM functionality allows organizations to nurture customer relationships, track sales leads, and enhance customer service.
Functionality of ERP systems
To drive efficiency and productivity for the above functions, ERP systems rely on shared underlying functionalities, which include:
- Data storage: serves as a centralized repository for all crucial business data, providing easy access and a single source of truth for decision-making.
- Process automation: automates repetitive tasks, reducing human error and enabling employees to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Reporting and analytics: provides real-time reporting and analytics, empowering users with valuable insights to make data-driven decisions.
Limitations of standalone ERP systems

Although ERP systems help organizations manage many business processes, even powerful flagship software has its limitations. Here are some instances where standalone ERPs might struggle:
- Inability to address specific business needsStandalone ERP systems are built to cater to general business processes, so they may not fully align with an organization’s unique requirements or industry-specific workflows. As a result, businesses may contend with inefficiencies and manual workarounds needed to adequately address their niche business needs.
- Lack of integration with other systems:Standalone ERP may be isolated from other essential business systems, leading to data silos and fragmented processes. This lack of integration restricts the flow of critical information, resulting in problems like stale data and informational blind spots.
- Difficulty in adapting to changing business requirements:Organizations must adapt swiftly to evolving market demands. Standalone ERP systems may lack the flexibility and agility needed to respond to new challenges and opportunities. Reconfiguring a massive, organization-wide system is like trying to steer a heavy cargo ship — it doesn’t spin on a dime.
Integration will allow your organization to overcome the limitations of standalone ERP systems, for improved efficiency, data accuracy, and decision-making.
What’s ERP integration?
ERP integration refers to the process of connecting and synchronizing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system with other software and systems within an organization. This creates an interconnected infrastructure that allows different applications to work in harmony.
Purpose of ERP integration
The primary goal of ERP integration is to establish a cohesive digital ecosystem where data flows easily between systems. By integrating ERP with other systems, businesses ensure critical information is readily available to relevant stakeholders, avoiding duplicate data entry and reducing manual efforts.
Types of systems that can integrate with ERP
Thankfully, ERP systems are designed with extensibility in mind. Here are three fundamental types of systems that can be integrated with ERP:
- Integration of CRM systems with ERP
Integrating your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) application with your ERP ensures that both systems synchronize customer information, sales leads, and real-time interactions. This enables sales teams to access up-to-date customer data, streamline the sales process, and deliver personalized customer experiences. If you’re not sure where to begin, Spinnaker Support offers personalized planning and execution for customized CRM-ERP integration. - Integration of e-commerce platforms with ERPFor businesses that operate e-commerce platforms, connecting to your ERP systems is paramount for efficient order management and inventory control. This integration enables easy order processing, inventory updates, and real-time tracking of sales data.
As customers place orders, the data automatically synchronizes between the e-commerce platform and the ERP system, ensuring accurate inventory levels and minimizing order fulfillment delays.
Moreover, financial data related to sales and payments are automatically updated, streamlining accounting processes and improving financial reporting.
- Integration of manufacturing systems with ERPManufacturing data such as work orders, bills of materials, and production schedules are synchronized with the ERP system, enhancing inventory visibility and facilitating accurate planning. This integration makes it possible for manufacturers to respond to changes in demand, improve production efficiency, and reduce downtime.
Benefits of ERP integration
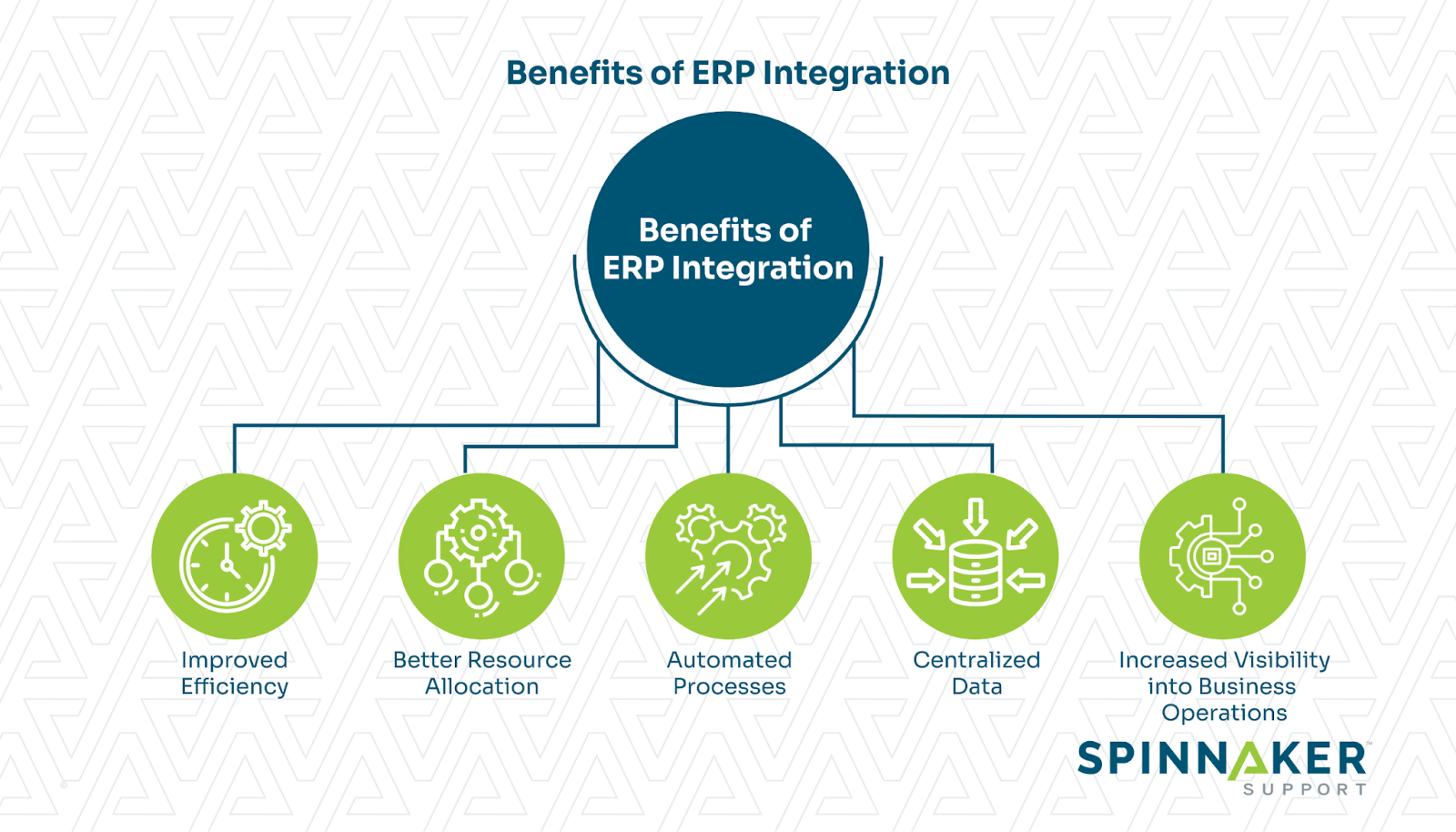
ERP integration can revolutionize how organizations operate and make strategic decisions. Here are the key benefits of using an integrated ERP system:
- Improved efficiency: ERP integration streamlines business processes by reducing manual interventions, duplicate processes, and manual data entry.
- Better resource allocation: With an integrated ERP system, organizations gain better insights into resource utilization across different departments. This enables more intelligent resource allocation, optimizing workforce productivity and ensuring resources are allocated to areas with the highest impact.
- Automated processes: ERP integration automates critical functions, such as inventory management, order processing, and financial reporting. Automated workflows improve accuracy, speed up operations, and reduce human errors, resulting in smooth, error-free processes.
- Centralized data: An ERP system serves as a centralized repository for data from across departments and functions. Establishing a single source of truth for data ensures accurate, real-time information is accessible to all relevant stakeholders, which promotes informed decision-making and collaboration across the organization.
- Workflow visualization: Organizations gain enhanced visibility into business operations through ERP integration. With intuitive dashboards and customizable reports, decision-makers can visualize workflows, identify bottlenecks, and make real-time data-driven decisions.
How to integrate ERP with your existing software operations

Integrating your ERP system with existing software operations is vital for creating a well-oiled digital ecosystem, but how do you actually do it? Here are the key approaches used to integrate ERP with your existing systems:
- Leveraging APIs for data exchange
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are the connectors used to allow separate applications to “talk to” one another. APIs are vital to integration because they facilitate data exchange between applications within your organization’s tech stack, such as when connecting your ERP to a Supply Chain Management (SCM) tool.Using pre-built tools and custom commands, your IT team can program APIs to call for the necessary data from the application. Once your APIs are set up, they serve as a gateway for data consistency between your applications.This means that changes made in an outside system are instantly reflected in the ERP system and vice versa. This real-time synchronization guarantees all stakeholders can access the latest information, enabling agile decision-making and enhanced collaboration across departments.
- Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)Leveraging an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solution further simplifies ERP integration. iPaaS provides pre-built connectors and workflows, making the integration process faster and more efficient.
With iPaaS, businesses can minimize development efforts, accelerate project timelines, and reduce overall integration costs.
- Enterprise Service Busses (ESBs)
Enterprise Service Busses (ESBs) offer a scalable and robust solution for organizations with complex integration requirements. ESBs act as middleware facilitating communication and data exchange between disparate systems, including the ERP system.ESBs can handle large data volumes and support different formats, making them suitable for enterprise-level ERP integration projects. - Custom development for unique needs:Every organization has unique requirements and existing software landscapes. In cases where pre-built solutions may not fully meet integration needs, custom development may be needed to build new tools from scratch. Custom integration is generally more time-consuming and costly, but it also offers the greatest level of power and flexibility to ensure that specific business workflows, data transformations, and security requirements are addressed.
- Strategic ERP integration with Spinnaker Support:ERP integration can be complex, but businesses can simplify the process and improve operations with help from a third party provider like Spinnaker Support.
Spinnaker Support offers comprehensive ERP integration services, leveraging APIs, iPaas, ESBs, and custom development to tailor solutions to your organization’s needs. With experienced engineers and a wide range of third party support services, businesses can easily navigate the integration landscape and unlock their ERP system’s full potential.
Factors to consider before integrating

Before integrating an ERP system, there are several factors you must consider to ensure the process is as seamless and beneficial as possible. Your approach to integration has real consequences for your system’s functionality and your business’s bottom-line, so it’s advisable to plan carefully. If your team lacks experience in these areas, you should consider hiring, upskilling, or investing in expert third party support.
Here are the considerations to bear in mind before integration:
- Business requirements and objectives:It’s imperative to ensure that your integration strategy is rooted in your organization’s objectives and needs. Your software decisions should be based on your business initiatives rather than being constrained by your enterprise provider’s roadmap. This strategic approach empowers you to tailor the integration to enhance your unique processes and address your pain points effectively.
Partnering with experts like Spinnaker Support amplifies this advantage. Their tailored approach to ERP integration recognizes that every organization has distinct goals.
- Scalability and flexibility of systems:A strategic approach to ERP integration can help increase the lifespan of your SAP software while building functionality to extend interoperability. This ensures that your ERP system remains adaptable to evolving business demands, technology advancements, and industry changes.
- Data security and privacy concerns:
Consider the sensitivity of the data being exchanged and ensure the integration complies with industry regulations and privacy standards. Sensitive data should be security with encryption and tight access controls. Spinnaker Support offers a comprehensive approach to security to proactively prevent and combat cyber threats. - Availability of integration capabilities and resources:
Evaluate the availability of integration capabilities within your ERP system and the other applications you intend to integrate. Determine if APIs or other integration tools are readily available and assess the expertise needed for successful integration. Consider partnering with an experienced third-party provider, like Spinnaker Support, who can help with integration resources. - Cost considerations and ROI analysis:
When evaluating ERP integration, factoring in the upfront costs and long-term financial benefits is essential. Choosing the right integration strategy can lead to significant advantages, such as freeing up bandwidth for executing your organization’s unique roadmap, rather than being tied to the timeline provided by SAP or other ERP providers.Gartner reports over 50% immediate savings with Spinnaker Support and up to 90% savings over time. By reducing spending on support, you can free up funds for other business-critical IT initiatives, such as cloud migration.
Best practices for successful ERP integration

Successful ERP integration requires meticulous planning and execution. Here are best practices that can be employed to guarantee a smooth ERP integration process:
-
- Thorough planning and assessment of integration needs:Start the integration process with a comprehensive planning phase that thoroughly assesses your organization’s needs. Engage all stakeholders, including end-users, to identify essential integration requirements, pain points, and objectives. This collaborative approach lays the groundwork for a well-aligned integration strategy.
- A clear understanding of data mapping and transformation requirements:A well-defined data mapping plan ensures that information is accurately exchanged between integrated systems. Ensure you understand the data flow between systems, the required transformations, and how data will be synchronized. Evaluate the technical mechanisms used for data exchange, such as APIs.
- Testing and validation of integrated systems:Conduct rigorous integrated systems testing to identify and resolve potential issues before going live. Verify data accuracy, system performance, and end-to-end functionality to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruption to business operations.
- User training and change management strategies:
Prioritize user training to ensure that employees understand the integrated systems and how to leverage their capabilities effectively. Implement robust change management strategies to foster a positive attitude towards the integration and ease the transition for all stakeholders. - Continuous monitoring and maintenance of integration processes:
Establish monitoring mechanisms to track data synchronization and system performance and identify anomalies. Regularly review and optimize integration processes to align with evolving business needs.
Leveraging the expertise of a reliable ERP integration partner can significantly enhance the success of your integration project. Spinnaker Support offers comprehensive support for the integration journey, from planning and design to implementation and post-implementation maintenance.
Conclusion
Embracing ERP integration has the potential to revolutionize your organization’s operations and propel you toward success. Integration is no small undertaking, but by understanding the nature of the challenges and following the best practices outlined above, you’ll be able to set yourself up for success.
Don’t wait any longer. Take the first step towards ERP integration and request a consultation with Spinnaker Support today.


