Quick Summary
If you’re an IT service provider, you’ll need to know the difference between ITSM and ITIL and how they’re implemented in modern organizations. We’ll cover everything you need to know here.
Introduction
Effective IT service management (ITSM) is critical for any modern enterprise to succeed in today’s digital landscape. The purpose is to optimize IT service delivery, keep IT in line with your business’s goals, and satisfy clients.
One of the most popular IT service management frameworks is the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL). But what’s the difference between ITSM and ITIL? And how do you implement them in your company?
This article will examine ITSM vs. ITIL, covering their definitions, components, and lifecycles in modern enterprise IT environments. I’ll also highlight the relevance of ITIL in contemporary enterprise IT management and briefly touch on other notable ITSM frameworks.
What is ITSM?
IT service management (ITSM) is a strategic approach to designing, delivering, and managing IT services in an organization. It’s a combination of processes, functions, and roles that work together to efficiently deliver IT services.
The primary objective of ITSM is to ensure your business has the proper processes in place to manage the entire lifecycle of IT services.

The key processes involved in ITSM include:
- Incident management: This process aims to quickly restore service operations to their usual performance levels after an interruption. Its focus is minimizing the adverse effects of incidents on business operations, ensuring optimal service quality and availability.
- Problem management: This process centers on detecting, logging, and addressing the underlying causes of IT incidents. It’s about fixing issues at their roots to prevent recurring problems, which can help increase the overall performance of IT services.
- Service-level management: This is where you document, monitor, and improve the level of IT services. It helps to align operational services with the business requirements by creating Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that are agreed upon with the customers.
- Change and release management: This process manages and controls changes to the IT infrastructure, including software releases, in a coordinated way. The goal is to minimize the impact of related incidents and reduce the risks associated with changes.
- Service request management: This process handles user requests that typically involve minor changes, such as a request for a new password or installing a new workstation. It ensures efficient resolution of requests to maintain user productivity and satisfaction.
- Configuration management: This process involves identifying, controlling, and tracking all the individual components of an IT system (known as Configuration Items or CIs) and maintaining accurate information about them. It provides vital support to other ITSM processes by providing accurate information on the IT infrastructure.
Now, let’s look at what ITIL is and how it differs from ITSM.
What is ITIL?
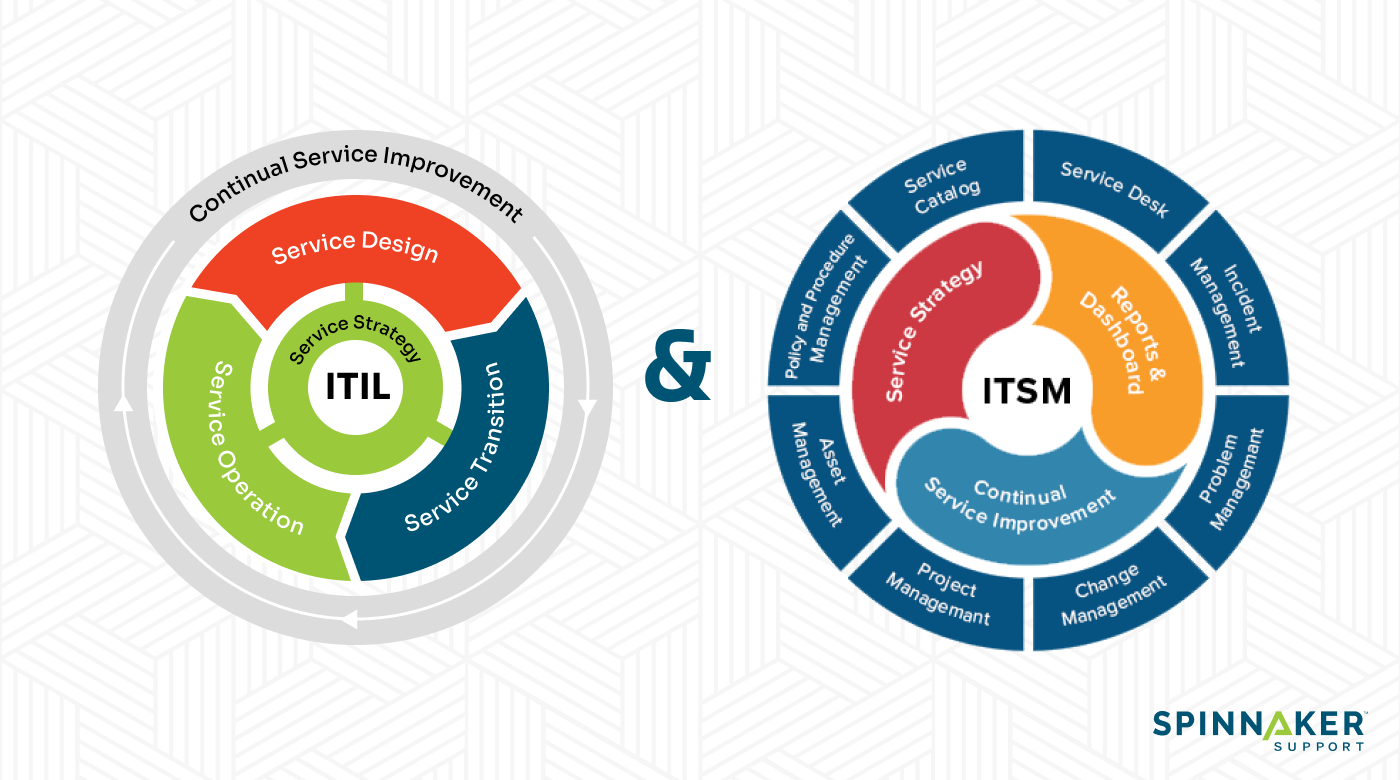
The IT Infrastructure Library, or ITIL, is a collection of ITSM best practices. These standard practices provide a framework for organizations to align their IT services with the business strategy and manage them effectively.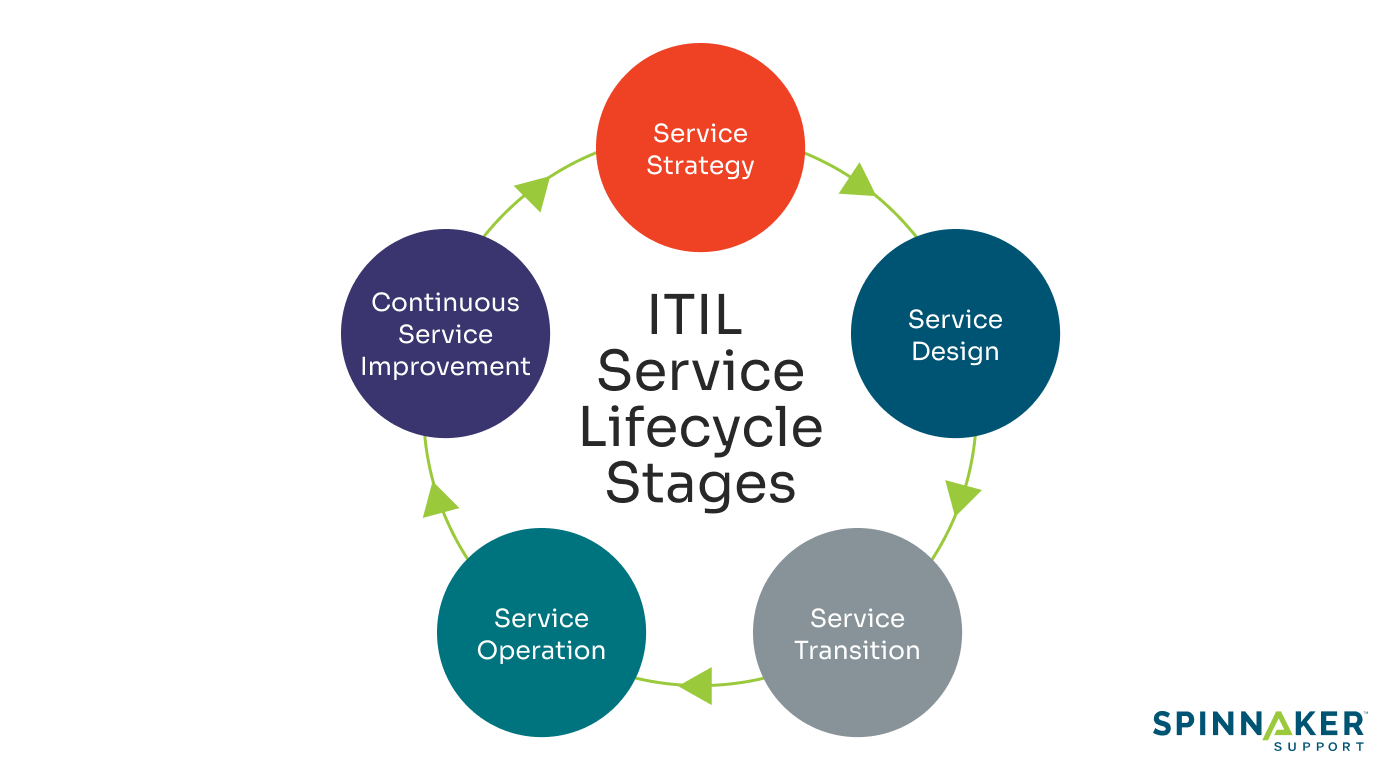
The ITIL framework is organized into a lifecycle model, which consists of five stages. Each stage focuses on a different aspect of service management:
- Service strategy: This stage involves understanding the customers and providing value to them through IT-enabled services. It helps organizations make strategic decisions on investments and organize resources effectively.
- Service design: This stage revolves around developing services that meet the business objectives identified during the service strategy stage. It also includes designing new and efficient IT services and processes or changing existing ones to support the service lifecycle.
- Service transition: This stage focuses on building, testing, and implementing services into production. The goal is to ensure a smooth transition for new or updated services with minimal disruption to business operations.
- Service operation: This is the stage where you deliver services to customers and measure the results. It involves managing the service value chain on a day-to-day basis and ensuring the efficient delivery of service.
- Continual service improvement (CSI): This stage uses quality management methods to learn from past successes and failures. The objective is to continually improve IT services and business processes.
In addition to these lifecycle stages, ITIL also delineates various levels of IT support to structure the workflow of service requests and incidents from initiation to resolution.
Let’s take a look:
ITIL support levels
ITIL support levels streamline the support process, optimize resources, and ensure relevant and experienced personnel handle issues. It allows you to segregate the severity of issues and follow a more efficient resolution process to improve service quality.
- Level 0 support: This is a self-service level where users can resolve their issues using online resources such as knowledge bases, FAQs, or user manuals. It’s the first point of contact for users and gives them immediate access to information without interacting with the service desk.
- Level 1 support: At this level, a help desk team provides basic technical assistance to end-users. It typically handles straightforward issues like software usage inquiries or common problems with known solutions.
- Level 2 support: This level provides operational support for more complex issues that can’t be solved at Level 1. Personnel in Level 2 support have a deeper understanding of the software solutions, operating systems, and hardware components in the organization’s IT infrastructure.
- Level 3 support: At this level, specialized IT personnel provide product and service support. They have in-depth knowledge of specific parts of the organization’s infrastructure and assist when problems require more technical expertise.
- Level 4 support: This is the highest level of support and involves third-party vendors or manufacturers. Level 4 support experts have a deep knowledge of specific systems or software. They’re typically called in to handle specific or complex problems that can’t be resolved internally.
Difference between ITSM and ITIL
Both ITSM and ITIL are sometimes used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences and uses in the realm of IT management.
The key difference is that ITSM is the philosophy of how to manage IT services, and ITIL is one way to put this philosophy into actual practice.
ITSM is a broader concept for delivering and managing IT services. It’s a strategic approach to ensure that IT systems deliver value and support business objectives. It’s analogous to the concept of Agile in project management, which is a general methodology that you can apply in diverse ways across different contexts.
On the other hand, ITIL is a specific framework that gives you detailed procedures, processes, tasks, checklists, and guidelines to implement ITSM. It’s similar to Scrum, which is an explicit set of rules to implement the Agile methodology for project management.
Relevance of ITIL in modern enterprise IT management
As an IT professional, you must adapt to modern methodologies like DevOps and Agile to tackle the rapid pace of the tech industry. But you might still be asking, “Where does ITIL fit in?”
The answer lies in ITIL’s ability to complement agile practices.
ITIL’s future isn’t about battling modern frameworks; it’s about adapting and integrating with them. Take Agile, for instance. Agile promotes swift and iterative development, which you might feel is a stark contrast to ITIL’s structured approach.
However, Agile and ITIL can still work together well. While Agile focuses on fast-paced delivery, ITIL makes sure that services are aligned with business needs and managed efficiently post-deployment.
The same holds true for DevOps, which promotes collaboration between the Development and Operations teams. It may seem incompatible with ITIL’s defined processes. But DevOps practices are about continuous integration and delivery. ITIL can offer the necessary structure to manage these services over their lifecycle.
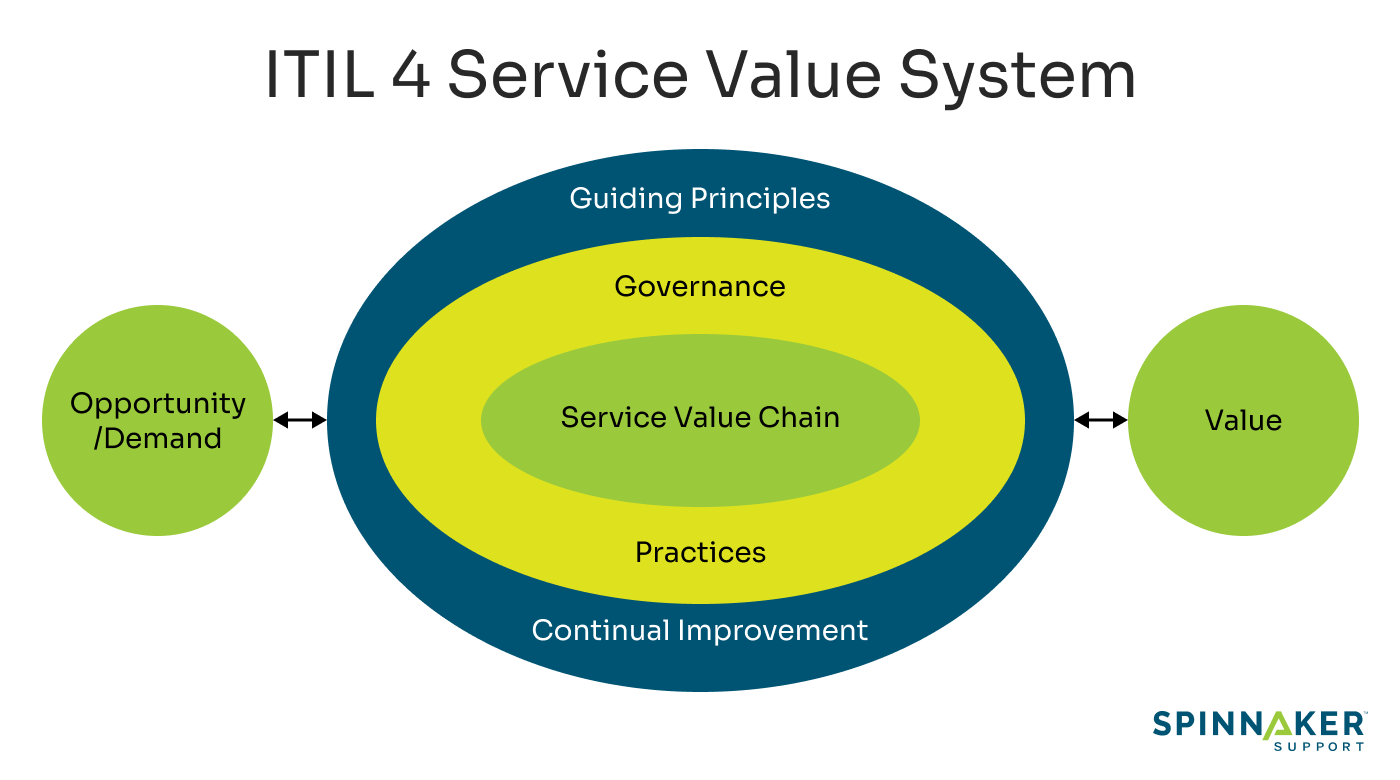
The key for ITIL is to shift to an adaptable approach that focuses on collaboration and business value creation. This is where ITIL 4 can play a significant role. ITIL 4, the fourth version of the ITIL framework, addresses some of the contemporary IT challenges and aligns closely with newer frameworks.
A prime example is the introduction of the Service Value System (SVS). SVS emphasizes that every IT service must start with an opportunity or demand, and the primary output should be value. This concept syncs perfectly with the principles of Agile and DevOps, where the end goal is to deliver maximum business value.
About 20% of organizations had already adopted or were using ITIL 4, and another 32.5% planned to do so. These figures underscore the growing interest in and relevance of ITIL 4 in the current ITSM industry. This adaptation doesn’t indicate a blind adherence to tradition but a recognition of ITIL’s intrinsic value and its ability to mesh with modern software development practices.
Brief overview of other ITSM Frameworks
While ITIL is certainly a key player in the ITSM space, it’s not the only one.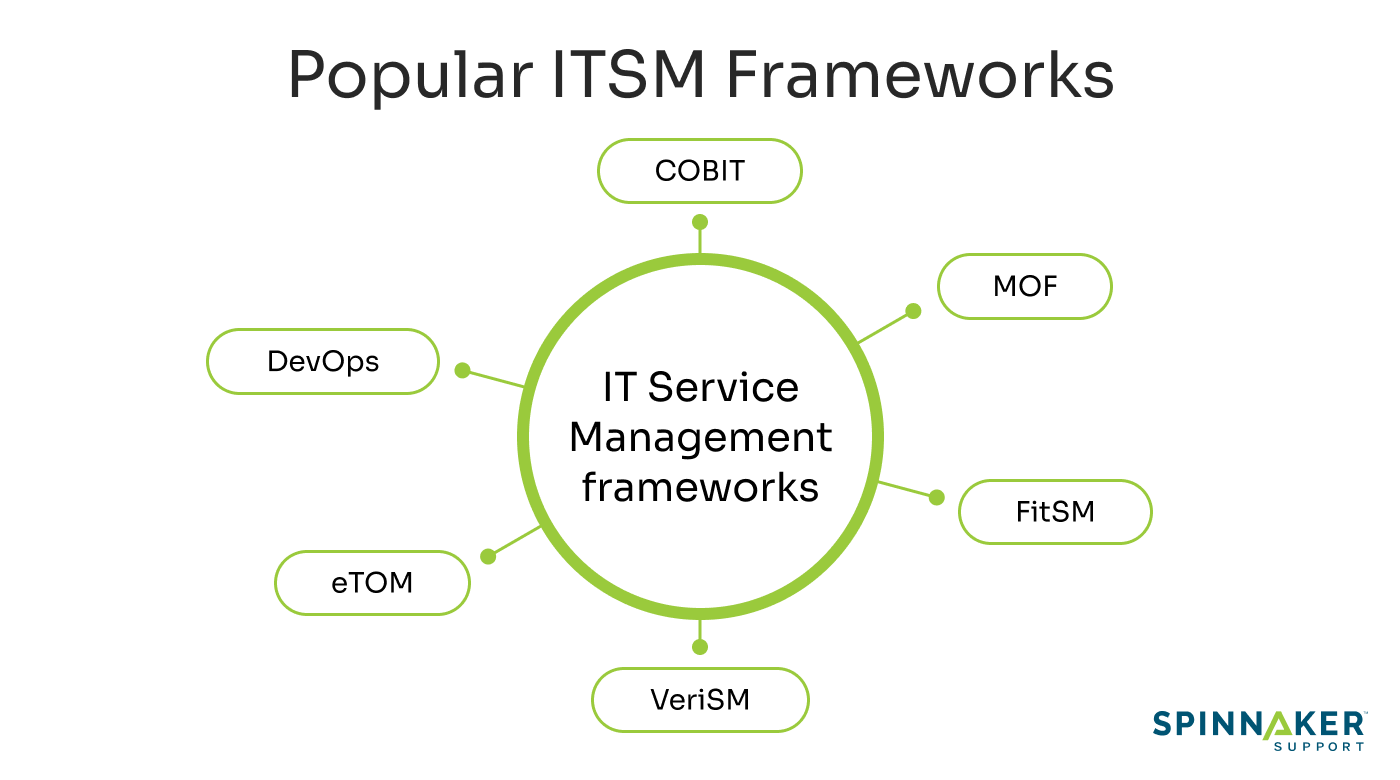
Let’s take a quick look at some other notable ITSM frameworks:
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): This is a robust IT governance framework that helps you align your IT operations with your business objectives. It’s particularly useful when risk management and regulatory compliance are key considerations for your organization.
- MOF (Microsoft Operations Framework): If your organization heavily relies on Microsoft technologies, then MOF is for you. It offers practical guidance for IT service management and primarily focuses on reliability and cost-effectiveness while aligning IT services with your business needs.
- eTOM (Enhanced Telecom Operations Map): eTOM is a comprehensive framework for managing telecom services. It provides a detailed mapping of all business processes involved in the telecom sector.
- FitSM: This is a lightweight and pragmatic ITSM framework. It’s perfect for organizations that are just beginning with a structured IT service management process. If you’re looking for a simple ITSM framework, this might be an ideal choice for you.
- VeriSM (Value-driven, Evolving, Responsive, Integrated Service Management): VeriSM advocates a tailored approach to service management based on the specific needs of your business and customers. It is the most flexible solution.
- DevOps: While it’s not a type of framework in the strictest sense, DevOps is a business culture that fosters collaboration between operation and development teams. This is a go-to choice for organizations whose aim is to ensure rapid and continuous delivery of IT services.
Ultimately, the key is to understand the strengths of each of the above frameworks, including ITIL, and leverage them according to your organization’s specific needs. Whether you choose ITIL, DevOps, COBIT, or any other framework, the fundamental goal remains the same — to deliver quality, business-aligned IT services.
Final Thoughts
ITSM and ITIL serve distinct roles when it comes to managed IT services. Each complements the other to ensure efficient and effective delivery of IT services in an organization.
While ITIL is the oldest ITSM framework, its latest edition, ITIL 4, has shown a promising capacity to adapt to modern needs. Other frameworks like COBIT, DevOps, MOF, eTOM, FitSM, and VeriSM also offer unique benefits depending on your organization’s specific needs.
At Spinnaker Support, we provide personalized, comprehensive third-party IT support and managed services to optimize your software ecosystems. Reach out to our expert engineers for unrivaled, personalized technical support for a range of products.


